
点击上方蓝字关注我们
Industrial Crops and Products
IND CROP PROD
2019年影响因子为4.244,审稿周期短,中科院1区,用户评分8.6,非常值得推荐!
期刊基本信息


期刊:Industrial Crops and Products
ISSN:0926-6690
影响因子:4.244 (2019)
出版周期:Bimonthly
Top期刊:是
Industrial Crops and Products is an International Journal publishing research on cultivated plants (crops) of industrial interest (non-food, non-feed). Papers concern both crop-oriented and bio-based materials research. It should be of interest to an international audience, hypothesis driven, and repeatable. Crops and products of interest include: fiber, forest, and energy crops, industrial oilseeds, rubber and resins, and cultivated medicinal and aromatic plants. The plant(s) in the manuscript must fit our definition of industrial crops, before it is classified further in research topics as indicated below.
期刊官网:http://www.elsevier.com/wps/find/journaldescription.cws_home/522825/description
投稿网址:https://www.editorialmanager.com/INDCRO
期刊涉及范围
作为一本农林科学领域国际权威期刊,主要接收关于具有工业价值(非食品、非饲料)的栽培植物(作物)的研究,涉及面向作物和生物基材料的研究相关主题的文章。
Research on food, phytochemistry, ethnobotany, and medicine are not in the scope of the journal. Authors should make clear in the cover letter how the research fits our scope following the detailed scope description below
1. Industrial crop management practices to increase productivity and specific chemical components. Including cultural practices (sowing, plant density, fertilization, pruning, shading, management of wild stands for sustainable harvest, pests and weed management, harvest, post-harvest, etc.).
2. Breeding and genetics of cultivated industrial crops. The research must be of international interest and hypothesis driven. The research must be of value to other breeders and the germplasm developed must be available to other researchers for further genetic improvement.
3.Response of cultivated industrial crops to abiotic (temperature, water, salinity, pH, heavy metals, etc.) and biotic stresses (insects, diseases, weeds).
4. Sustainable cropping systems including an industrial crop to reduce negative environmental impacts of conventional cropping systems. For example, cultivation in marginal lands, intercropping, double or relay cropping, cover cropping or other systems intended to minimize soil erosion, eutrophication, greenhouse gases emissions, loss of biodiversity, etc.
5.New techniques for the propagation of industrial crops or production of metabolites in vitro (root and tissue culture, micropropagation).
6. Discovery or development of new industrial crops is in the scope, but must include an evaluation of the real potential to make a plant an industrial crop, not just information on plants gathered in natural habitats (many plants make products, but they will not become a crop). An economic analysis may be included as appropriate.
7. Extraction methods of metabolites from industrial crops and waste streams of industrial crops processing (non-food related).
8. Biochemical and thermochemical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass.
9. Bio-based materials:
-Fiber and fiber compounds: cellulose-, hemicelluloses-and lignin-based products, textiles, nanofibers, composites, films, etc.
-Other crop-polysaccharides based materials such as carbohydrates and proteins-based products not intended for the food industry (adhesives, varnishes, paints, etc.)
-Rubber, waxes, resins, gums from crops
-Polymers from crops
10. Crop and forestry biorefinery:
-Energy crops: fuel (bioethanol, biogas, syngas), biochar, chemicals, etc.
-Oils, fatty acids, biofuels (biodiesel, jet fuel, drop-in fuels), and chemicals derived from oilseed crops
11. Biologically active compounds:
-Insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and pharmaceuticals (the species has to fit our definition of industrial crop; cultivated plants or plants with demonstrated potential to be cultivated with non-food purposes)
-Essential oils: inks, dyes, lubricants, perfumes, cosmetics, plastics, and other industrial applications
12. Bio-based products must be tied to specific crops/plants, and their modification to meet new industrial uses. For instance, for nanoparticles, a direct link is required with an industrial crop or with the respective value-chain.
13. In the manuscript, all species must include the Latin name and Authority, the first time the species is mentioned in the abstract or text.
期刊分区
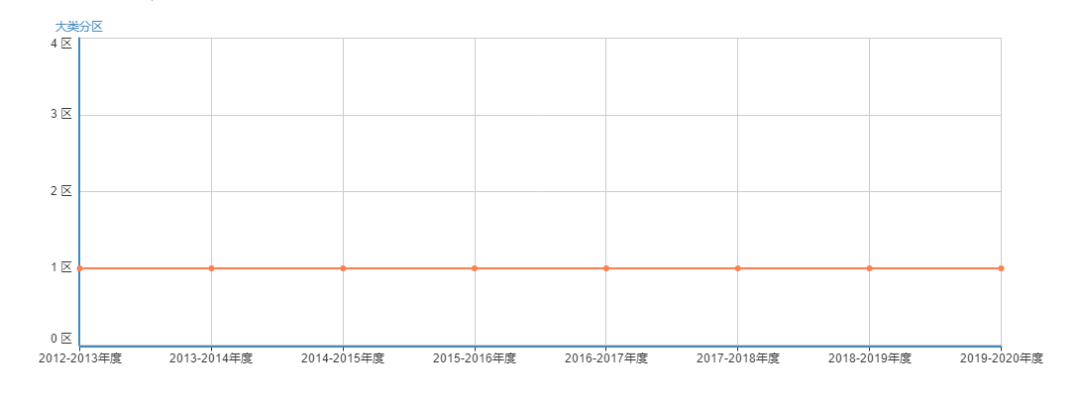
目前中科院基础版和升级版分区都在工程技术1区。
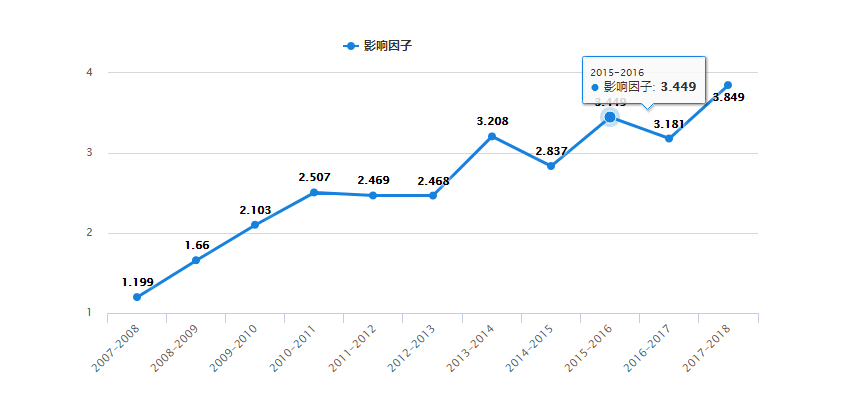
IF变动趋势图
这几年来Industrial Crops and Products影响因子整体保持不断增长的态势,2019最新影响因子已经达到4.244,预计今年即将公布的影响因子会有增长。
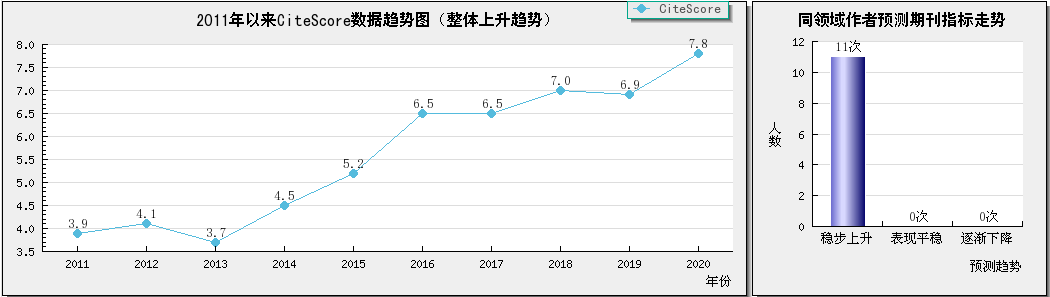
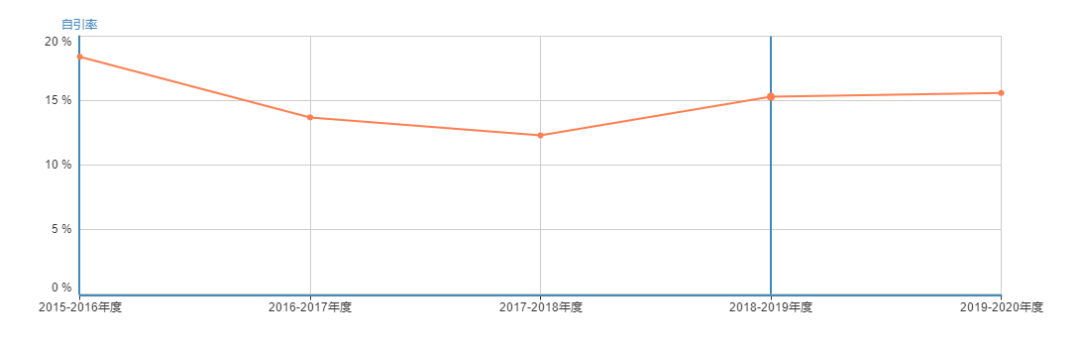
期刊cite score&自引率趋势图
期刊自引率:Industrial Crops and Products自引率一直在20%以下,最新自引率为15.6%。
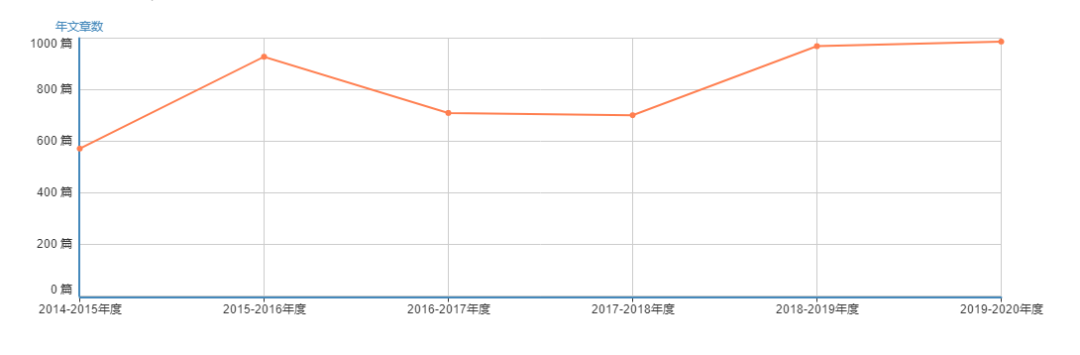
年刊文量/国人第一
年发文量及收稿范围:Industrial Crops and Products属半月刊,发文量常年保持在1000篇左右。
杂志审稿周期
平均审稿速度
网友分享经验:平均1.3个月
平均录用比例:网友分享经验:66%
来源Elsevier官网:平均4.7周
平均录用比例:来源Elsevier官网:16%
一起来看看本年度录用文章作者投稿经验分析:
Author 1:
研究方向:农林科学 遗传学
投稿结果:已投修改后录用
投稿周期:1.0个月
发表时间:2021-06-25
投稿经验:
3.21投稿;
中间格式有问题,语言问题直接让改语言,改完后返回;
5.12大修;
6.13返回意见;
6.16直接录用。
速度挺快的,质量挺好。
Author 2:
研究方向:工程技术 材料科学:复合
投稿结果:已投修改后录用
投稿周期:3.0个月
发表时间:2021-06-21
投稿经验:感觉还是很好的,审稿人加主编一共提了40条意见左右,都是蛮有用的,认真修改后,已经被接收。3.29投稿,6.20接收。
Author 3:
研究方向:工程技术 能源与燃料
投稿结果:已投修改后录用
投稿周期:3.0个月
发表时间:2021-06-05
投稿经验:
2021.3.9 submitted to journal
2021.3.10 with editor, 要求添加参考文献doi信息,之后再次上传
2021.3.16/3.18 with editor
2021.3.19/3.25 under review
2021.4.2/4.13 required reviews completed
2021.4.15 decision in process
2021.4.16 major revision, 四个审稿人,领域内专家视角,提了四五十条意见,问题深度很好。认真修改论文,回复意见大概17页,内容和逻辑性感觉提高了不少。
2021.5.11/5.16 with editor
2021.5.17 under review
2021.6.2 required reviews completed
2021.6.4 accept
第一篇icp,杂志口碑很好,虽然影响因子不太高,但是地位稳固,明年影响因子接近5.5。很满意的一次投稿经历,感谢主编和审稿人。

Industrial Crops and Products
影响因子:高(4.244)
审稿速度:最快(1个月)
国人文章占比:高
自引率:低
Industrial Crops and Products 作为农林科学领域的老牌SCI期刊,知名度很高,国人认可度也很高。根据投稿作者反馈显示,期刊送审速度非常快;官网也显示平均2.5周即能收到初次投稿结果,5.5周即能确定最终接收与否,确定后平均3周以内就能上线,效率非常之高。期刊为非OA期刊,不收版面费;若选择OA出版,则需支付3560美元稿件处理费。
以上数据均来自网络,文章属于原创,限于水平有限,必有不对之处,欢迎批评指正,将虚心接受和改正。
最后祝大家科研顺利!
版权声明
本文由Websci Academic原创
欢迎转发本文至朋友圈,如需转载请标明出处。感谢支持!
公众号转载请后台留言联系
文献互助❖检索查询❖热门期刊
转载&合作咨询请联系
Websci Academic


